February 9, 2019 – Today’s guest contributor is Aaron Burdick, a resident of Louisville, Kentucky, proud pet owner of a golden retriever who he describes as his best friend, and a writer of articles about the environment, human rights, and quality of life issues. In this contribution he introduces us to Zoox, one of 62 companies in California that has received approval to test their autonomous vehicles throughout the state. As always your comments and feedback are invited.
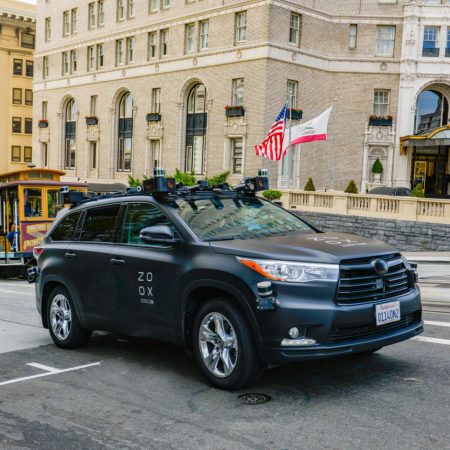
California has a reputation for embracing new technologies, especially evident in its policy towards self-driving vehicles. One of those technologies that has received approval is Silicon Valley-based Zoox, founded in 2014. The state has granted the company not only the right to test its technology on public roads, but also to transport passengers in its vehicles. This is a first for California.
Who is Zoox?
Zoox is building a 100% autonomous vehicle transportation service with a focus on passengers, not drivers. Their vehicles have no “front” or “back.” There is no steering wheel. Built specifically for safety, Zoox is focused on eliminating the human factor in driving and therefore, accidents.
With the California approval, Zoox is now expanding its operations from allowing only its employees and family members on its vehicles, to the general public. The company wants to hear from Californian commuters so that it can improve its self-driving technology.
Zoox is committed to sustainability, and therefore, all of its vehicles are zero emission.
Zoox Services Will Have Stipulations for Now
Before the company can achieve an absolutely autonomous vehicle service, California is requiring that at least one trained driver be onboard just in case of an emergency. The agreement also stipulates that the current operation of Zoox vehicles will be free to anyone who chooses to go for a ride in one of its vehicles. These restrictions fall in line with California’s Drivered AV Passenger Service pilot program, which lawmakers approved in May of 2018. Officially listed as Decision 18-05-043, the main requirement stipulates a physical driver on board at all times.
Along with this pilot, California has also issued a second called the Driverless AV Passenger Service program which could allow companies like Zoox to send their vehicles out without a physical driver on board. Under this California pilot, the DMV requires the company to have employees constantly monitor their vehicles from secured locations. In addition, every vehicle must include a way for passengers to get in touch with the employees who are tracking the vehicle. Although no Zoox vehicles have been given the green light to operate this second pilot, it is likely that Zoox will be the first to be granted this privilege, all things going well.
Who is the Competition?
Zoox is just one of 62 autonomous vehicle companies operating in California. But one, in particular, stands out as a prime competitor. That is Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet that started in 2009. Waymo has been testing its autonomous vehicles without drivers in many California cities, but to-date they are not allowed to pick up passengers.
Waymo, however, has been operating with greater freedom in Arizona. Just recently, it announced that customers in Phoenix could pay a fare to use its self-driving vehicles. While many Waymo vehicles have a human driver on board, a few now are driverless. Testing has been ongoing for several months.
Autonomous Vehicle Safety Issues
When discussing the pros and cons of autonomous vehicles, critics most often question safety standards. It’s no wonder this is an issue since the press seems to cover any autonomous vehicle crash turning these rare occurrences into global headlines. The latest occurred in Tempe, Arizona, when an Uber’s self-driving vehicle fatally struck a pedestrian during a test-run. After this tragic accident, Arizona’s Governor ordered Uber to stop testing its self-driving vehicles on public streets.
As of today, there is no clear evidence to indicate that autonomous vehicles are safer than those operated by human drivers. The sample is far too small. Only putting more autonomous vehicles on the road both with and without a human driver will produce enough data to better understand the technology’s safety issues.
In the meantime, many who are technology savvy have suggested research into engineering ethics to address public fears. Through the specifying of autonomous vehicle behavior acceptable to the public, it will help companies like Zoox and Waymo to improve on their self-driving algorithms.
Other Issues Facing The Industry
Safety concerns will always be the most significant issue surrounding autonomous vehicle technology. But there are other challenges. For instance, vehicle accident attorneys are grappling with changing the laws governing accidents to account for this technology. With different degrees of autonomy in most self-driving vehicles, lawyers are trying to figure out how much liability should be assigned to drivers or manufacturers in the event of a crash.
There’s also a concern that autonomous vehicles cause significant changes to the automotive industry. The growth of the sharing economy, some economists believe, will make autonomous vehicles more attractive to ride-share companies than to private consumers. To increase safety and reduce both traffic and emissions, it’s more likely that self-driving vehicles will be operated as fleets owned by the manufacturers, or by transportation businesses rather than be purchased by individuals. If this comes to pass then car dealerships and the service industry that is currently the business model around the world will drastically change. That means dramatic disruptions to post-vehicle manufacturing jobs. On the flipside, a shift to shared autonomous vehicles will mean more people will be spending time looking at screens while in transit, and that may prove a boon to advertisers.
California’s DMV Standards For Driverless Vehicles
To address some of these issues, CA DMV has been formulating autonomous driving regulations since the beginning of 2013. Currently, there are three different tests to which autonomous vehicle companies can apply: testing permits with a driver, driverless testing permits, and public use permits. You can learn more about these at the California DMV website. The full text of the California autonomous vehicle regulations is available at California Vehicle Code Section 38750. And for a list of current autonomous vehicle permit-holders, check out the official webpage.