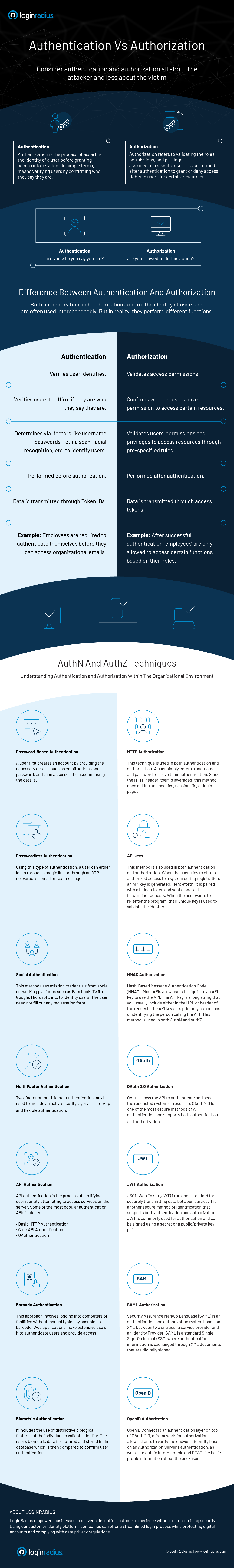
July 14, 2020 – The terms authentication and authorization get bandied about in the world of computing. They are often used interchangeably and are key to managing identity and access. They are instrumental to an organization’s data integrity, ensuring that only the right people get access to sensitive information. While authentication confirms a user’s identity, authorization determines what that user can see.
Types of Authentication
There are three categories of authentication that can be deployed by a business. Here comes some of that jargon that the title of this article indicated as being pervasive in the industry. But these are important terms to know.
- Single-factor authentication is as the name suggests. It provides a means of validation that involves a user having to get his or her password right.
- Two-factor authentication adds another layer to single-factor authentication by introducing an additional step after a password is correctly entered. Typically it involves a question that only he or she knows the answer to.
- Multi-factor authentication is used by banks and other highly sensitive businesses to eliminate any possible data exposure.
- Single sign-on (SSO) provides a master authentication routine letting a user access different computer applications with one set of credentials.
Types of Authorization
Authorization can be categorically classified as well.
- Role-based access control is a straightforward means of authorization used whenever there is a need for system-to-system and user-to-system privilege management.
- Public/private key pair specifically recognize a user’s private key with a corresponding public key residing on a protected server. Without a match, authorization is denied.
- OAuth authorization system uses API authentication which sends an application key and secret to a login page which if correct provides a user with a token that is subsequently recognized by the system being accessed as legitimate.
- Digitally Signed XML Documents use Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), an open standard for exchanging authorization data.
Despite differing in significant ways, all of these processes serve a common purpose, to identify persons seeking access to secure systems. Using a number of them is the best way to protect organization’s from cybercriminals, an ever-present and growing threat.
To learn more about authentication versus authorization, check out the infographic that follows created by LoginRadius.