There are so many stories to choose from in any given week but the following are ones I thought you might find interesting. They include a new breakthrough in biomedicine, a number of stories on energy, and one on pollution and the environment. The headlines read:
- Biosensor Detects a Single Cancer Protein – What Does That Mean?
- Preliminary Fracking Report Gives Technology a Clean Bill of Health;
- Oil Sands Creating Thousands of Environmental Problems in Alberta;
- Bill Gates Backs Nuclear Power That Uses Spent Fuel to Generate Energy;
- China Spending $277 Billion to Attack Urban Air Pollution.
Microcavity Biosensor Developed to Detect Cancer Marker Proteins
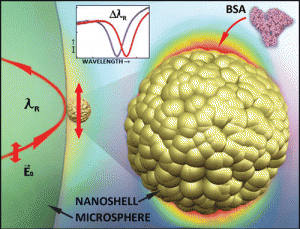
Finding and interrupting cancer causing triggers is a noble enterprise. A combination of researchers from the Polytechnic Institute of New York University, Department of Physics, Fordham University and the Department of Biological Sciences at NYC College of Technology have created a nanoshell biosensor capable of detecting a single protein marker for thyroid cancer. Their research appears in NANOLetters. The biosensor is a remarkable technology that can find an object like a protein, a mere one-sixth the size of the smallest virus.
What this means for early cancer diagnosis is astonishing. States Stephen Arnold, one of the researchers in the study, “Proteins run the body…..when the immune system encounters virus, it pumps out huge quantities of antibody proteins, and all cancers generate protein markers. A test capable of detecting a single protein would be the most sensitive diagnostic test imaginable.” The biosensor, seen below, features a gold nanoshell that can be detected when laser light reflects off it and gets picked up by a remote receiver. When the cancer marker clings to the nanoshell the light frequency changes making it possible to identify it from a blood sample within minutes.
U.S. Department of Energy Study Gives Fracking a Clean Bill of Health
The Marcellus Shale formation, which underlies Pennsylvania, New York, Ohio and West Virginia, has been a key area of oil and gas exploration using the technology known as hydraulic fracturing or fracking. Numerous reports in the past have indicated that fracking may contaminate aquifers and freshwater sources. But researchers after a year-long study have found no evidence to support claims of pollution from fracking operations.
In the study conducted by the Department of Energy, drilling fluids containing unique trace markers were injected into gas well bores thousands of meters below the surface. Drinking water sources and surface water testing within 1.6 kilometers (1 mile) of the well bores showed no trace markers. One of the scientists participating in the study, Rob Jackson of Duke University, cautioned that this is a single study of a single well and doesn’t prove that fracking is not a pollution risk.
One study finding showed that a fracture (see image below) reached as far as 550 meters (1,800 feet) from the well bore. No one had suspected fractures to extend that far. The study also showed that all fractures stayed well below the aquifer boundary from which drinking water was sourced.
Are We the Victims of an Oil Sands Cover Up?
In the last week the Toronto Star reported that fewer than 1% of environmental infractions related to the Alberta oil sands have led to a provincial response. The evidence appears in a 677-page report that has been peer-reviewed but is not yet published in any academic journal.
One of the co-authors, Kevin Timoney, a biologist and environmental consultant, described finding thousands of breaches of environmental regulations dating all the way back to 1996. These included spills into the Athabasca River, random waste dumps in the boreal forest areas surrounding oil sands operations, and smokestack emissions that exceeded environmental safety standards. Of the total infractions, 66% involved sulphur dioxide and hydrogen sulphide emissions exceeding regulatory limits. About 20% involved failing to report contraventions of provincially set standards. 7% were water infractions and 1% land issues.
The Government of Alberta’s enforcement rate in responding to the number of incidents, a mere 0.9%. The median fine was $4,500. When compared to U.S. enforcement related to the Clean Water Act violations of 8.2%, Alberta’s policing of the oil sands can only be described as pitiful to non-existent.
If Bill Gates Backs It Does That Mean This Type of Nuclear Plant Will Get Built?
I have written about the promise of new nuclear power plants in the past involving technology like that being developed by TerraPower, a company backed by Bill Gates of Microsoft fame. Called a Traveling-Wave Reactor or TWR, the technology uses depleted uranium fuel as its energy source ignited by a cap of enriched uranium. It requires no maintenance, no spent fuel disposal and would operate autonomously for between 50 and 100 years once loaded with fuel, generating up to 1,000 Megawatts of electricity. A 600 Megawatt test-bed reactor is scheduled to be built within the next 10 years. The advantage over current nuclear reactor technology – a TWR uses the spent fuel rods of light water reactors as its energy source helping to clean up what is considered one of the biggest downsides of the industry today. Gates has shown the TWR technology to TED participants and has also met with the China National Nuclear Corporation about building one of these reactors in that country.
China Throwing Hundreds of Billions of Yuan at its Air Pollution Problems
When China with its centrally-planned economy takes on climate change action they don’t put in chump change. According to the China Daily, China’s Ministry of Environmental Protection is enacting a plan to control airborne pollutants. The total investment from the government – 1,700,000,000,000 Yuan ($277 billion U.S.) over a 4-year period.
The plan will begin with Northern China as its focus looking at reducing emissions by 25% from 2012 levels. This will improve air and water quality in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province. What will be involved? That closing of factories that are heavy air and water polluters with utility companies, petrochemicals and automotive enterprises the principal targets.
The pollution that blanketed Beijing in January this year focused the government on the environmental problem making them realize something had to be done. The investment to clean up polluters should be offset by the development of new green industries which will further boost the economy by an estimated 2,500,000,000,000 Yuan ($407 billion U.S.), much more than the total spent in implementing the plan.
A Postscript
Are you working with a breakthrough technology? Would you like to see it reported here? Then let me know. As always I thank my thousands of readers for continuing to visit these pages and look forward to your many comments and questions. Thanks for dropping by.
– Len Rosen