My weekly picks unlike last week are not a single theme but range over many science and technology fields. I hope you find these stories as interesting as I do.
- The Universe is 100 Millions Older Than We Thought;
- Physicists Calculate Doomsday Argument;
- New 3D Display No Longer Requires Glasses;
- Wireless Blood Testing Eliminates Needles;
- UK Company Begins Mining Nodules on Sea Floor.
Planck Telescope Reveals An Older Universe
First published data from the 15 1/2 months of Planck telescope mission observations gives us a revised estimate of the age of the Universe. No longer 13.7 billion years, it is now 100 million years older. Planck (seen in the image below) is mapping cosmic background radiation by filtering out interference from stars and galaxies. The latest data has given us a picture of what our Universe was like 370,000 years after the Big Bang. From this data we have revised estimates on its make-up. Matter, the things we can see like stars, planets, nebula and galaxies account for 4.9%. Dark matter represents 26.8% and enigmatic dark energy, the balance, at 68.3%.
Calculating Doomsday for the Human Species
Oh what fun! Apparently physicists with nothing better to do have been calculating the future of our species. It is a common premise among scientists to argue that enduring civilizations are rare. But there is little in the way of science to back this up. So a group of researchers at University of Oxford decided to tackle the problem in greater detail by factoring in nuclear war, asteroid impacts, climate change, global pandemics, and unknown threats. Their conclusion is less gloomy than the Doomsday Clock that nuclear scientists hatched in the 1950s always showing the minute hand creeping closer and closer to the midnight hour. The Oxford team also offered suggestions to improve our chances of survival including the following:
- developing technologies to divert Earth-crossing asteroids
- combating climate change
- exploring space and establishing off-world colonies
HP Labs Develop 3D Display
Researchers at Hewlett-Packard are moving us closer to the holodeck of Star Trek with the development of 3D displays that don’t require us to wear dorky glasses. The technology involves a modified liquid crystal display (LCD) just like the one on your high-definition television, smartphone, flat-screen computer display or portable gaming device. Where conventional 3D provides a viewer wearing glasses with one perspective, HP 3D gives the viewer the ability to walk around an experience the image from many viewpoints. This multi-view capability comes from changes made to conventional LCDs. HP’s display has patterned nano-grooves with three sets of grooves for red, green and blue light.
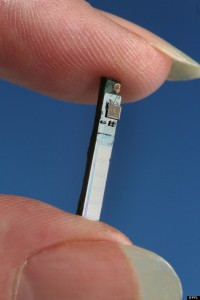
Wireless Blood Testing May Make Needles a Thing of the Past
Patients with illnesses that require constant blood tests will appreciate the potential implications of this technological innovation on their lives. Researchers at the Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne in Switzerland have developed a personal blood testing laboratory, a few cubic millimeters in size with a built-in Bluetooth. It can be implanted just under the skin to read vital blood signs which can then be read by doctors using computers, tablets or smartphones. The current prototype detects five proteins and organic acids simultaneously. It can detect chemical changes that predict a heart attack hours ahead of time. For diabetics it can continuously measure blood sugar levels and send alerts. Or it can be used to monitor patient blood chemistry during cancer chemotherapy. The inventors state that they can potentially “detect just about anything.” The implant is so small it is easy to place or remove. Currently being tested in animal studies it is hoped that it will be available within 4 years for human use. So say goodbye to needles and all those vials of blood.
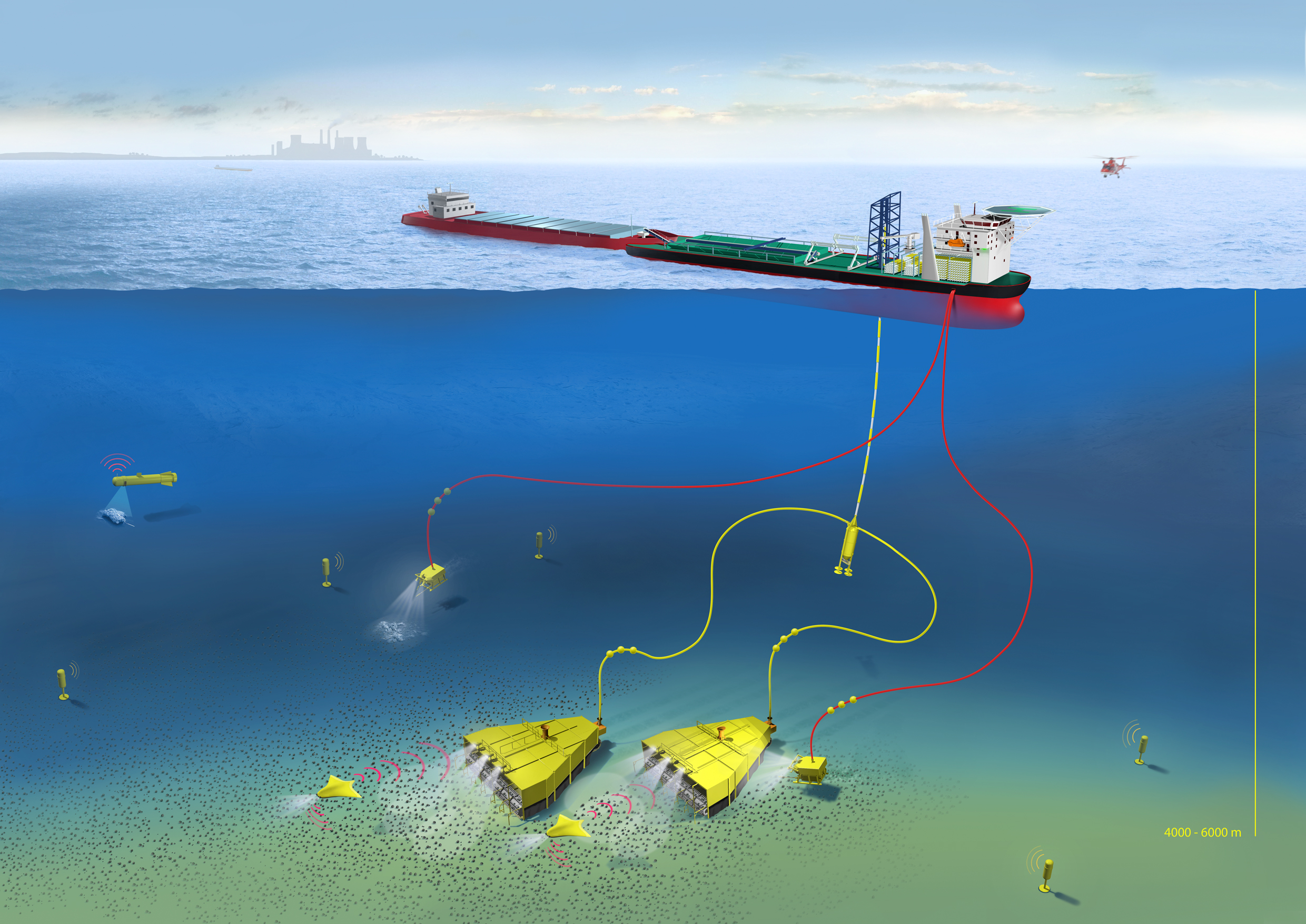
UK Company About to Mine Nodules from the Sea Floor
For many years we have known about manganese nodules littering the deep sea floor. In truth there is more than manganese to mine at the bottom of the ocean. The nodules are also rich in nickel, copper, cobalt and rare earths. Now Lockheed Martin UK plans to harvest nodules from a 58,000 square kilometers (22,400 square miles or about the surface area of Lake Michigan) of the Pacific Ocean seabed 1,500 kilometers (about 950 miles) southwest of Mexico. Operations are expected to begin within 5 to 6 years. Nodules vary from the size of golf balls to potatoes. The technology to be deployed would be a combination vacuum-rake that would gather the nodules which then be ground into a slurry for pumping to surface ships. Environmentalists are concerned that any disturbance to sediments at the bottom of the ocean could irretrievably harm seafloor communities. That’s why the operation is delayed so that data can be gathered about the ecology in the harvest zone to ensure the environmental impact is minimized.
A Postscript
Comments, questions and ideas for postings are always welcome. If you come across a technology you feel should be part of this conversation please let me know by writing to info@21stcentech.com.
– Len Rosen