Welcome to this week’s 21st Century Technology headlines. Each week I select a few interesting stories about technological innovation that can help us tackle the problems we face this century. As always I encourage you to comment, ask questions and provide input on topics I write about or feature. This week focuses on computers that can read lips, the latest cold fusion news for both skeptics and believers, cyborg bugs for search and rescue, and a symposium and plans for a 100-year starship.
Artificial Intelligence Update: Computers Being Taught to Read Lips
In “2001: A Space Odyssey,” the astronauts fail to realize in a private conversation that the HAL computer could read their lips. Subsequently events unfolded in dramatic fashion. That was science fiction. Now for the reality.
Scientists in Malaysia are teaching computers to interpret human emotions by following lip and facial patterns. Their research has been published in the International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. The computer is not just being taught to read lips, but to understand through human facial expressions, human emotions. Using a “genetic algorithm” that keeps getting better with each iteration, the computer is capable of recognizing happiness, sadness, fear, anger, disgust and surprise. Hope that means no surprises for all us intelligent life forms going forward.

Energy Update: After Zurich Conference on Cold Fusion We Remain in the Dark
Andrea Rossi, the idol of the cold fusion community, talked a lot in Zurich, at the much anticipated September 8 conference, about a working, commercial, cold fusion reactor. But “talking” is the operative word. Rossi held up a paper from an independent third-party contracted to test the E-Cat cold fusion device called the Hot Cat. Results of these tests, Rossi claimed, showed net energy produced amounting to 3.6 kilowatts for every 1.28 kilowatts of input, roughly a 3:1 ratio.
Measuring energy output and input remains a challenge for the industry. Is a 3:1 return better than what we get from damming a river to generate hydro? I’ve tried to find ratio measures for different energy producing technologies and hope one of you, my readers may have found a source you can share with me. Then we could compare apples to apples.
But getting back to the Rossi Hot Cat results, a day after the conference, Hydrofusion Ltd., a company that is a licensee of Rossi’s E-Cat, stated in a press release that it had witnessed independent tests of the Hot Cat on July 16th and August 17th, and could not support any claims made, “written or other, about the amount of excess heat generated.”
Now I know that those who are followers of cold fusion are going to get your shorts in a knot, but once again, Rossi, as the leading spokesperson of the LENR community, continues to fail to demonstrate an independently verifiable, workable device. And once again, for those who will send me comments stating I don’t know what I’m talking about, all I say is show me. I’m not from Missouri but would welcome reviewing a demonstration, a scientific paper, a real device that actually is marketable. Because if it works then LENR opens a world of possibilities.
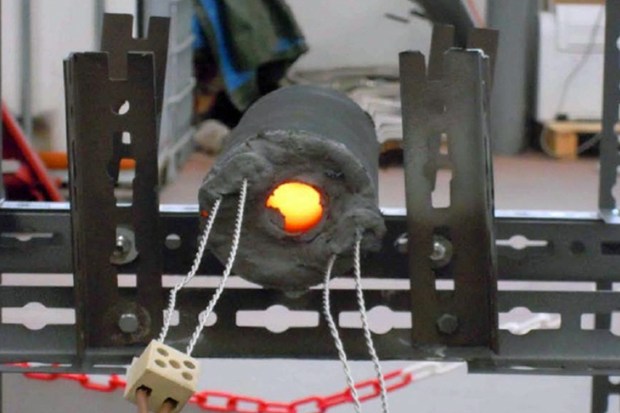
Robotics Update: Cockroach Cyborgs Can Go Places No Human Has Gone Before
Building bio-mimetic robots is one way to take advantage of what evolution has already proven works. But another way is to take an animal and add bot technology to it to create a cyborg. That’s what engineers at North Carolina State University are doing with the Madagascar Hissing Cockroach, saddling it with a backpack of electronics that includes a micro controller, wireless receiver, and battery pack. Wired into the roaches antennas, a sent signal guides the insect where the sender wants it to go. It could be called riding the roach just like being on horseback.
Why a roach? Because roaches can get around. A roach can slip into a building after an earthquake and traverse the wreckage to spot survivors. A roach can enter a hostile environment and provide surveillance. A roach can get into pipes and walls. And roaches are durable, surviving in extreme conditions. Isn’t that why we hate them?

Space Update: Symposium Looks at the Next 50 Years of Spaceflight
The 100-Year Starship Symposium began its meeting in Houston on September 13 of this week to discuss a very big idea – interstellar travel. With seed funding from DARPA, the symposium is bringing together engineers, political leaders and scientists to study the feasibility of building a starship within the 21st century to travel to our nearest stellar neighbour, Proxima Centauri. At 12% the speed of light, such a ship would take 50 years to reach this red dwarf star approximately 4.24 light years from Earth. Former American President, Bill Clinton, has signed on as honorary chair because he believes the technology to drive humanity outward will also provide benefits for those who remain here on Earth.
Two Greek myth-inspired project ideas, one from the 1970s, called Project Daedalus, and its more recent successor, Project Icarus, will certainly be discussed. Both projects conceived of building an enormous fusion-powered spaceship for interstellar flight.
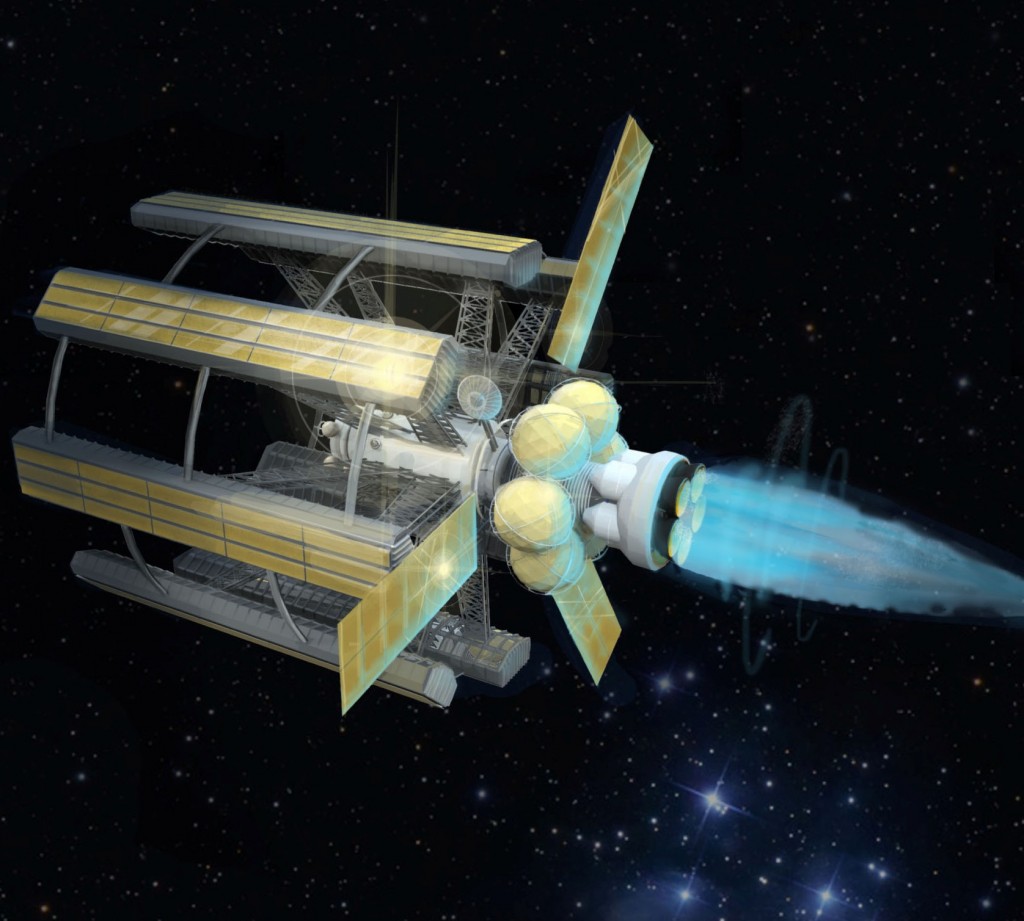

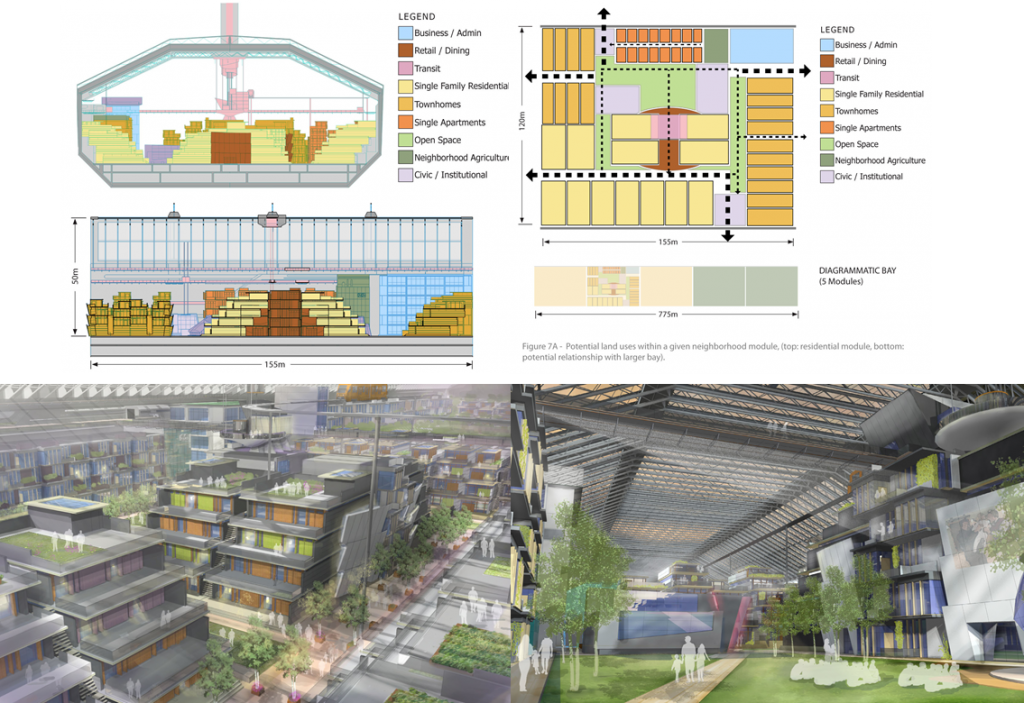
The spaceship, seen in the artist rendering above, is the one proposed for Project Icarus. It would consist of an enormous banded cylinder with habitation bays (the long rectangular yellow objects) connected by pedestrian viaducts (the spokes). The ship would rotate around a central zero-gravity core which would also be connected to the engines and the central power generators. Design specifications propose a radius of 400 meters (approximately 1,300 feet), and a length of 775 meters (over 2,500 feet) for each of up to five habitation modules. In full compliment the spacecraft target population would be 10-12,000.
A self-contained environment, seen in the artist depictions below, as well as two images of the design, show an artificial world where inhabitants could wander several kilometers on a walk through highly variable neighborhoods joined by transit spokes. Diverse housing styles and accommodation would create a variable interior landscape with lots of “green” space and open courts. The internal habitat would be reconfigurable to provide variety for the space travelers on their long voyage to the stars. A fantasy? Maybe, but those convening at this symposium see this as a future 21st century reality.
A Postscript
Readership continues to climb. Thank you for inspiring me to continue to write.
Some of you may have come to 21st Century Tech through my Facebook site. If you did please go back and “Like” the Facebook page. I’m getting close to the 30 “Like” readers to give me access to analysis of reader traffic through that site.
To the many thousand of you who continue to visit here each month, and to all of you who are here for the first time, thanks for dropping by and keep on coming back. You can do this by subscribing so that you receive every new posting in your email inbox.
For your efforts I promise to keep you interested and intrigued about 21st century technology and our future. – Len Rosen








