February 21, 2018 – From artificial intelligence to 3D printing to quantum computing, the following are the technologies that the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has picked as its choices for 2018 breakthroughs. What’s not on the list: reusable rockets, global satellite Internet access, 5G networks, and autonomous vehicles. Despite that these picks are very much pushing the technological envelope.
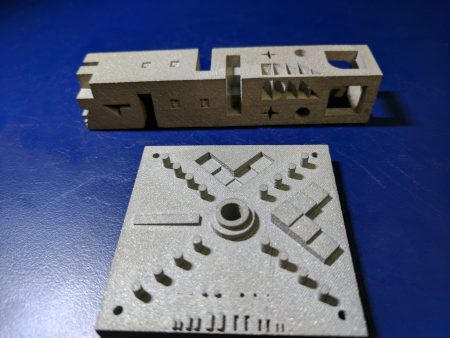
1. 3D Metal Printing
Printing objects is becoming commonplace with 3D printers under $1,000 becoming consumer products. The materials these printers use are largely plastic resins. But the value proposition for manufacturing lies in printing metal and its impact on both mass and made-to-order production. The term industry uses is additive manufacturing.
Companies like Markforged and Desktop Metal are driving additive manufacturing forward using metal inks. These companies are recent entries into the printing business and have attracted considerable interest from early investors. Meanwhile, industry stalwarts such as HP and GE see 3D metal printing as opportunities to exploit with their long-time customer bases. Elon Musk’s SpaceX uses 3D printing to build rocket engine nozzles and fuel tanks.
For tool and die companies like Magna International, 3d metal printing will be disruptive. Expect the automobile industry in 2018 to begin transitioning away from suppliers who don’t jump on the 3d metal printing bandwagon.
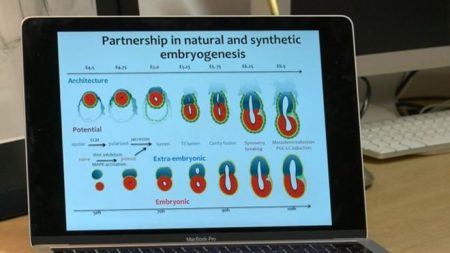
2. Artificial Embryos
Stem cell technology is making it possible for embryologists to create embryonic life without an egg or sperm. Using stem cells, University of Cambridge researchers in the United Kingdom have produced synthetic mouse embryos which like natural ones, self-organize and divide. The next step state researchers is to duplicate the experiment with human stem cells to create embryos for laboratory study.
Through this breakthrough, medical researchers will better understand embryonic development, and even devise better fertility treatments for couples having trouble conceiving.
The researchers at Cambridge noted that all they created so far is the embryo. What’s still missing is a life-supporting yolk sac or placenta to nourish their creation. The latter will likely also be created using stem cells.
There is another side to creating viable embryos from stem cells. Will 2018 be the year in which the first human is cloned?
3. Sensing Cities
If given the opportunity to pick a 2018 breakthrough technology, this would be one of my favourites. Google’s parent, Alphabet, has through Sidewalk Labs, begun collaborating with the City of Toronto, to develop Quayside, a downtown site that is a rethink of urban neighbourhoods. Described as more than a smart city, Quayside will incorporate the latest digital technologies including networks of sensors deployed in buildings, sidewalks, light poles, roadways….you name it, designed to gather data about everything. From air quality to noise levels, Quayside intends to deliver in the end an urban Eden in the heart of a metropolitan area with over 5.9 million people.
In Quayside all vehicles will be autonomous and shared. Robots will be deployed to do chores from trimming grass to delivering the mail and pizza. The software created from the project will be open access so that companies providing services and technology products will be able to build applications that will be fully integrated. Google is even building its Canadian headquarters in the heart of the new community. That’s how vested the company is in creating the sensing city. And San Francisco, Denver, Los Angeles, and Boston, are all clamouring to become the next guinea pig for Sidewalk Labs and their own Quayside equivalents.
4. AI for Everyone
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been one of the hottest topics in technology discussions in 2017. There is an abundance of articles in the media arguing both for and against efforts to develop machine-learning software and neural network computing. Some futurist prognosticators claim we are about to launch an assault on humanity by further AI dabbling. Elon Musk fears AI ascendant and has created his own company to tame the worst extremes of an overbearing machine intelligence in our future.
But AI for everyone is a thing today whether you are talking to a Siri or Ask Google on a smartphone, or asking Alexa or a Google home assistant about today’s weather. The companies bringing AI to everyone include Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Apple, and China’s Baidu. They are playfully introducing AI based in the cloud, making it possible for everyone to experience the technology.
Google has created a suite of systems called Cloud AutoML (the ML stands for machine learning) that are pretrained to make using AI easier. Microsoft has created Azure, its cloud AI platform. Amazon has Gluon, an open-source machine-learning library.
5. Dueling Neural Networks
Neural networks are a form of AI that attempts to replicate how the human neurons in the brain work. The idea of dueling neural networks involves pairing two of them together in what is called a generative adversarial network (GAN). By pairing these networks and having them both looking at the same data sets, a GAN can discriminate between what is real and what is fake from paintings to money, recognize pedestrians in their many forms to give autonomous vehicle systems better visualization and reaction capability, detect differences in voice recognition, and even produce more realistic computer speech.
The ultimate GAN will lead to AI with a sense of imagination, and with the ability to understand the nuances of what it sees in the world. For autonomous cars, it means the ability to self-train by imagining thousands of likely scenarios when in traffic without actually having to go on the road to experience them.
The development of GANs will give machines the ability to dream. See the image below.

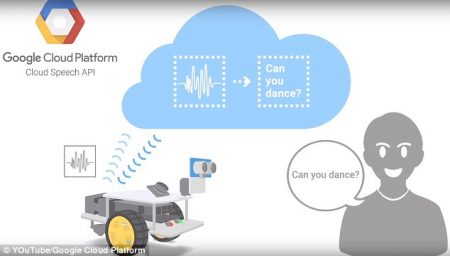
6. Universal Translators
Introducing Pixel Buds from Google, a set of earbuds that work with Pixel smartphones and Google Translate to produce an instant translation. When a person wearing the earbuds speaks in his or her language, the smartphone app translates the speech and broadcasts it through the smartphone. The person on the receiving end can then speak to the phone with the translated words heard by the earbuds wearer. To eliminate the conversants talking over each other, the wearer of the Pixel Buds taps and holds his or her finger on the right earbud when beginning to talk.
It’s not quite the Star Trek universal translator, but for $159 U.S. it is a true leap forward.
7. Zero-Emission Power from Fossil Fuels
Natural gas has been described by the former President of the United States, Barack Obama, as a transition fuel for power generation, as we move to a carbon-free energy world. And the move away from coal to natural gas thermal power generation is the main reason the United States has been able to lower its net annual carbon emissions over the last few years. But natural gas is not a carbon-free fuel even though it is abundant and cheap.
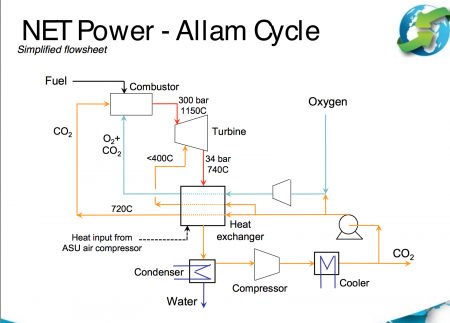
Making it zero emission would help everyone on the planet in our effort to tackle climate change. That’s what NET Power, a U.S. company claims it can do not by capturing and sequestering carbon emissions post-combustion, but rather by creating a new power technology and process that is virtually emission free.
NET Power calls this breakthrough technology the Allam Cycle, invented by Rodney Allam. It uses a high-pressure, oxy-combustion burning the natural gas with pure oxygen rather than ambient air. That eliminates nitrogen and nitrogen-based airborne pollutants from the post-combustion stream. Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture is part of the core power generation process with CO2 produced in combustion recycled back to the combustor multiple times until it produces pure CO2 under high pressure in liquid form. That CO2 is the working fluid that drives the turbine in the power plant. The CO2 becomes the fundamental source for heat exchange in what is a nearly closed-cycle system. The excess CO2 produced is easily captured for repurposing in commercial products such as cement and plastics, or sequestered underground.
Currently, NET Power is testing its technology at a 50-megawatt power plant near Houston, Texas. Could this technology be adapted for use with coal as the fossil fuel source? If so its deployment globally would be an environmental game changer well beyond 2018.
8. True Internet Privacy
Zero-knowledge proof is a cryptographic protocol developed for Zcash, a digital currency launched in 2016. The creators of this Bitcoin alternative created zk-SNARK, an anonymous transaction protocol. The acronym stands for zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge. What zk-SNARK does is protect privacy for the individual engaged in a Zcash transaction ensuring that each transaction is invisible to the general public.
Needless to say, the banks are interested in the potential to use zk-SNARK for secure payment systems. One of them, JPMorgan Chase, has added the technology to its own blockchain-based payment system. The main drawback is speed. zk-SNARK is computation heavy and slow like so many applications running on blockchain. Speeding it up will be the key to turn it into a true game changer. That is already starting to happen in 2018.
9. DNA Report Cards from Birth
It is less than two decades since the human genome was first fully mapped and now we have the means to provide a genetic report card which will give each of us risk scores for the most common diseases. If you haven’t yet tried 23andMe or AncestryDNA then you may not fully appreciate the implications of the revolution that is occurring.
From predicting risk factors for cancer, Alzheimer’s, and other gene associated diseases, to likely IQ scores based on genetic markers, we are entering the age of what pharmaceutical companies and genetic scientists are called polygenic risk scores, the ability to summarize a person’s genome measuring liability to specific disorders or traits.
You may not like receiving a DNA report card but the parents of newborn babies may receive one automatically at birth. Having a polygenic risk score in the form of a DNA report card could save the lives of millions in the near future, or help medical professionals intervene before early onset of a disease indicated by genetic markers.
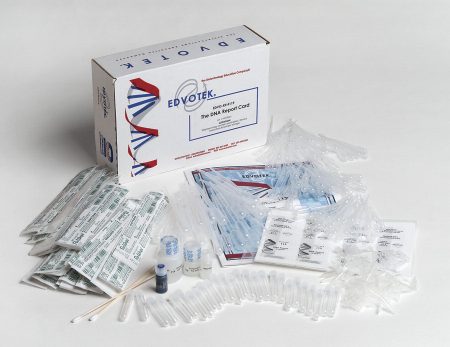
Want to try doing a DNA report card for yourself? Student kits like the Edvotek DNA Report Card (seen in the image below) are available on the market today.
10. Quantum Computations Solving Real Problems
The problems with quantum computing to-date are two-fold:
- There are only a limited number of these computers in the world.
- There is limited software to do much with them.
But one application is beginning to stand out as something that quantum computers could do really well. That is, designing molecules, new proteins, novel electrolytes, new drugs, better batteries, and more. In other words, helping to create new materials that can be used in a wide range of applications.
Researchers are stymied by existing computers when it comes to modeling molecules or simulating their behaviour. But quantum computers are effective in handling the nuances, the shades of grey that are not possible with technology that is built on either a “0” or a “1.” The only thing limiting the complexity of our new molecular discoveries is the size of the quantum computers available to us today.
Leading the pack in quantum computing development are Google, Microsoft, IBM, and D-Wave. As more qubit capacity is put into these very capable computer systems we will see a revolution in our ability to study and develop new materials for thousands of applications. In 2018 we will be well on our way.
So these are MIT’s picks for the year. They are all interesting technologies that will be further discussed in future postings at this site.
If you have candidates for a technology or scientific breakthrough that you believe has been overlooked by the crew at MIT, please feel free to comment and share your thoughts here. Thanks for visiting 21stcentech.com and please come back.