July 25, 2017 – If the electric car is to become ubiquitous, then what Toyota is planning to introduce in a little more than four years may prove to be a game changer. Instead of electric vehicles (EVs) running on lithium-ion battery packs, they will, in future, run on solid-state technology.
Today’s lithium-ion (LiON) technology has limits: range, recharge rates, and recharge cycles. For example, a Tesla Model S has a range limit of 400 kilometers (250 miles) before recharge. With a fast charger, it can take 30 minutes for a full recharge. That’s pretty much state of the art for EVs today.
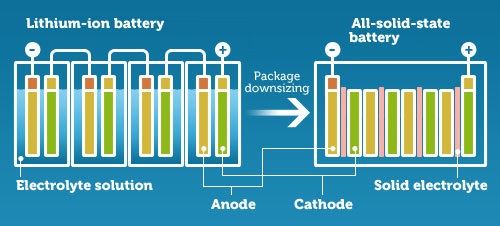
On the other hand, there are solid-state batteries which can extend range dramatically while recharging much faster. A solid-state battery of similar output to Tesla’s LiON could extend the car’s range two to three times. That battery would be smaller and lighter as well.
Other solid-state advantages:
- The batteries use solid electrolytes producing greater energy density in a smaller form factor. The large separators needed in LiON technology are not required. Instead solid-state has thin barriers to prevent short circuits.
- Solid-state is safer. These batteries do not experience potential hot spots caused by manufacturing defects in the separators leading to overheating. They will not explode or catch fire.

- Solid-state electrolytes are less reactive and hold a charge longer.
- There are many more material choices for manufacturers of solid-state batteries.
Solid-state batteries can be made using the following materials:
- lithium-halide
- perovskite
- lithium-hydride
- copper-zirconium-phosphate
- garnet-oxide
- argyrodite
- lithium-phosphorus-oxynitride
- lithium-super-ionic
And they come in two varieties:
- thin film
- bulk
Lithium-phosphorus-oxynitride, also known by the acronym, LiPON is a material suitable for thin film solid state. These batteries are ideal for watches, other wearables, and cell phones. After 40,000 charge cycles, a typical LiPON battery will lose a mere 5% of capacity. That means LiPON technology can last from 40 to 130 times longer than comparable LiON.
Garnet-oxide is a material suitable for bulk solid state. It can produce the same energy output as current LiON technology using a much smaller footprint while at the same time retaining capacity over many more charge cycles.
In all cases, solid-state recharges much faster than LiON. The batteries Toyota expects to use in its 2022 EV models will recharge in 5 minutes (about the same amount of time it takes today to fill a gasoline-powered vehicle fuel tank.) The batteries will retain 100% charge capacity over a minimum 1,200 recharge cycles outperforming LiON by 400%.
When you consider Toyota has not been a big adopter of LiON technology it is not surprising that the company is choosing a different route in the evolution of its EVs. The leap to solid-state will be dramatic. But in the interim, the company intends to continue producing its existing Prius and other brand-hybrid cars, a hydrogen-fuel-cell car, and in 2019 will begin manufacturing LiON-powered EVs in China.









