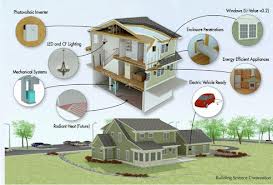
What is the ideal home? For most North Americans it is a single residential unit surrounded by a lawn and garden similar to the home that appears in the picture below.
But for the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), part of the United States Department of Commerce, who built the house pictured here, although appearing typical, this house is far from it. A two-storey, four-bedroom, three-bath standalone residence, it is located in Gaithersburg, Maryland. And unlike most suburban homes it has been built to meet LEED Platinum standards.
Unfamiliar with LEED? It stands for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design. First proposed in 1998 by the Green Building Council in the United States, LEED provides a framework for designing and building “green” buildings of all types. LEED examiners rate buildings on a point system with four categories: certified, silver, gold or platinum, the last being the highest standard. Points are given for site sustainability, construction materials, water and energy efficiency, and internal environment quality.
Called the Net-Zero Energy Residential Test Facility, this structure incorporates renewable energy-generating technology, construction materials that provide effective insulation, computer environmental controls, and has been built to be energy net-zero. That means a balance between energy from the grid offset by renewable energy systems in the house itself.
Features include:
- Walls and roofing insulated to twice the level found in homes currently being built
- A roof with no gutters to channel rainwater to a gravel perimeter connected by pipes to several bio-retention ponds
- Self-healing vapour and air barriers with a high-velocity air distribution system through both conventional and small ducts and a dedicated humidification and dehumidification heat recovery system
- Solar arrays capable of generating between 2.6 and 10.2 Kilowatts of electricity
- Solar water heating systems
- Geothermal heating and cooling systems
Designed for a family of four, the home is a laboratory testing ground to learn about optimal designs for residential construction. After one year of operation simulating four residents it is hoped that results will show energy net zero achievability. The public is invited to follow the performance of the house online at the NIST test site.
Although the house may be considered a typical residence in the United States, it is certainly much larger than most homes on this planet. Dimensions are:
- 252 square meters (2,709 square feet) not including the unfinished 140 square meter (1,500 square foot) basement
- Frontage width of 26 meters (86 feet) than most homes on this planet.
Typically, as a suburban home, it makes accommodation for the automobile but anticipates an electric vehicle by providing a charging station in the detached garage.
How will the energy exchange system work? On days when there is little sun the house will receive power from the energy grid. When the sun is out the solar arrays with DC to AC converters will provide the power for all lighting, heating and appliances. Last week marked the official ribbon-cutting ceremony. Check back from time to time to see if the goals of the design team have been met.